Polygon is a solution for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchains. It was previously known as Matic Network. Blockchain technology came to the real world with the introduction of Bitcoin. But Ethereum was the blockchain that showed enormous capabilities of the decentralized systems.
By introducing smart contracts, Ethereum showed that blockchain could do a lot more than just payment solutions. Decentralized applications that aimed to solve real-world problems emerged on Ethereum, and many of them became successful products. But there are still limitations to Ethereum and similar blockchains.
It’s the reason some projects have emerged to provide alternative solutions to dApp developers and the blockchain industry as a whole.
As Ethereum gained attraction and the network grew very fast, the problems and challenges showed themselves. Many similar blockchains were developed to solve the issues. Most of them are Ethereum-compatible which means you can migrate your Ethereum application to them and enjoy more benefits.
Creating these kinds of blockchains and connecting them to each other was a problem that Polygon aims to solve. It provides a protocol and a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchains. Now we can see why the project uses the tagline “Ethereum’s Internet of Blockchains.”
What is Polygon?
Polygon is here to solve lots of problems consistent with Ethereum and Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Consider the Ethereum-compatible networks as computer networks with similar fundamentals but different features and use cases. Connecting these networks can be a great solution for the bigger network.
Besides, when there is a platform for easy deployment of these networks, we can expect more businesses to try to connect to the bigger ones. Polygon provides various tools and features to manage these issues.
For example, one can easily set up a blockchain network using one-click presets in Polygon. Besides, there are numerous modules that help developers create custom Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
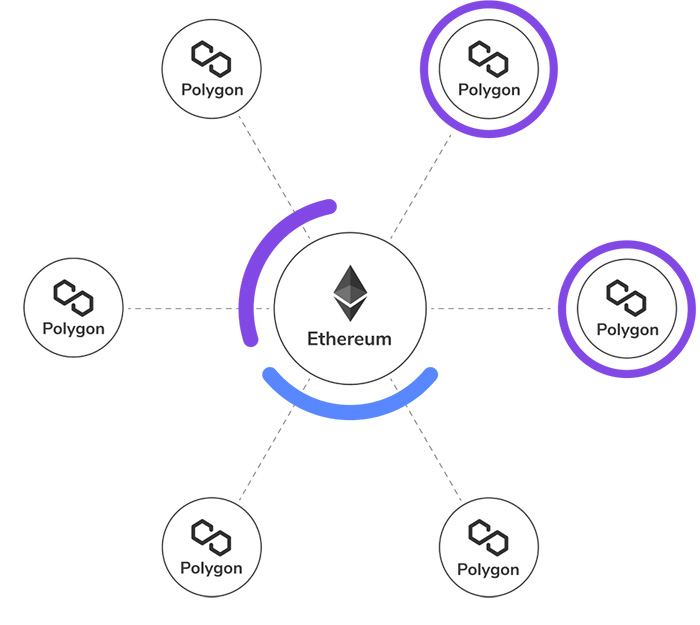
The comprehensive solution that Polygon offers focuses on expanding the Ethereum community. It helps developers design and deploy their own blockchains and connect them to each other to enjoy more benefits. There is an interoperability protocol in Polygon that makes it possible for new blockchains to exchange messages with the Ethereum blockchain. Besides, they can exchange messages with each other, too.
Security is a fundamental feature for every blockchain that wants to solve real-world problems. Polygon provides security features as security-as-a-service that helps developers deploy security features in a module-based manner. It also has many modules that help developers create interoperable blockchains with existing blockchains like Polkadot, and etc.
History of Polygon
As mentioned before, Polygon has first named the Matic network. A group of dApp developers created the open-source project as a solution for scaling in the Ethereum blockchain.
They used the fundamentals of the Plasma project and introduced a scaling solution with PoS sidechains. The team was successful in partnering with other big Ethereum projects likeDecentraland (MANA) and MakerDAO (MKR).
As time went on, the Matic team managed successful investment and support rounds from big names in the industry like Coinbase and Binance. Polygon is the new name for that successful project.
The founding team consists of experienced dApp developers, including CEO and Co-founder Jaynti Kanani, Co-Founder and COO Sandeep Nailwal, Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer, Anurag Arjun, and Co-Founder and enigmatic developer Mihailo Bjelic.
The advisory board is also filled with famous blockchain activists like Hudson Jameson from Ethereum Foundation, Pete Kim from Coinbase, and Ryan Sean Adams from Bankless.
Polygon Technology
As mentioned above, Polygon provides a framework and a protocol for easy deployment of blockchains with interoperability, security, and many more preset features.
Developers can create stand-alone blockchains that have the best of both worlds. In simple terms, blockchains that use the Polygon network can be private, having sovereignty, scalability, and flexibility features while benefiting from Ethereum features like security, interoperability, and developer experience.
As a result, they have a specific blockchain with special use-cases that can exchange messages with Ethereum and other Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
Polygon framework provides the tools needed for deploying Ethereum-compatible blockchains very easily. The Polygon team uses the “one-clock” term to show how easy it is to deploy a blockchain on Polygon. Besides, there are numerous modules ready to access in Polygon that help developers create a custom blockchain, for example.
You can deploy consensus, staking, governance, EVM, and many more features using modules in the Polygon framework.
Polygon protocol is the feature that makes the internet of blockchain a reality in the Ethereum community. It provides the features for arbitrary message passing between blockchains that are created on Polygon. As a result, the stand-alone blockchains will be connected to each other and the big Ethereum blockchain while keeping their privacy.
They can also benefit from the “security-as-a-service” tool in Polygon and make sure the network is kept safe while keeping the connections alive.
Polygon Chains
Developers can create two types of blockchains in the Polygon network. Stand-alone networks and blockchain networks that use the “security-as-a-service” module are supported in the Polygon framework. Each of them has specific features and benefits that we’ll discuss below.
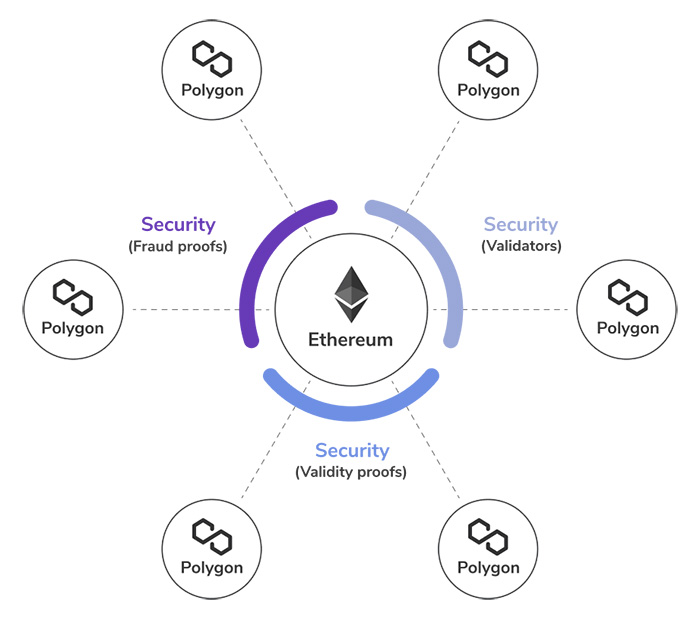
Secured Chains
Secured chains in the Polygon framework don’t have a validator pool. They use the “security-as-a-service” module in the framework.
The service lets developers use security features from Ethereum or a pool of professional validators. The latter is similar to the “shared security” feature in Polkadot blockchains. Securing a blockchain with preset trusted tools offers the high-level security that a developer may need.
But these secured chains have fewer capabilities in terms of independence and flexibility. Because they have to follow the security presets that Ethereum or other security pools offer.
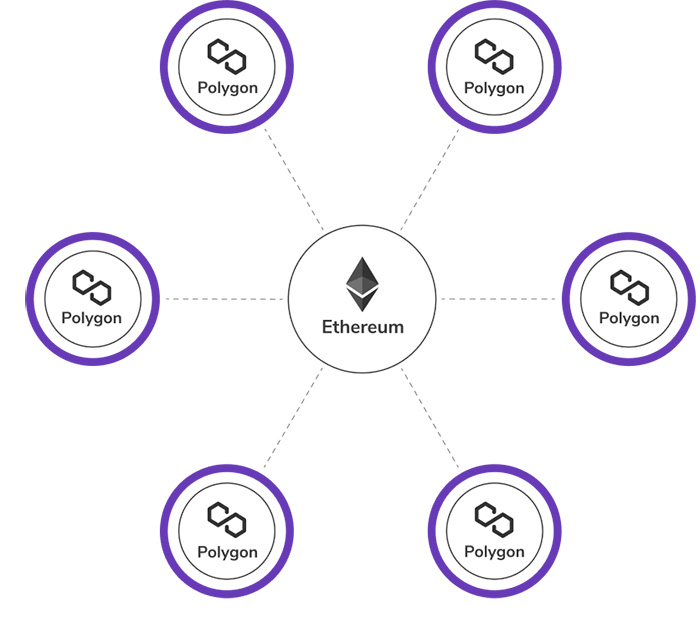
Stand-Alone Chains
Those developers that seek solutions for the sovereignty challenge in Ethereum can use stand-alone blockchains in Polygon. These blockchains are fully independent while being able to connect and exchange messages with other blockchains on Polygon.
As a result, their developers are fully in charge of security and other features for the blockchain. They have to establish validator pools. So, the full flexibility feature comes with more work for providing security in a stand-alone chain.
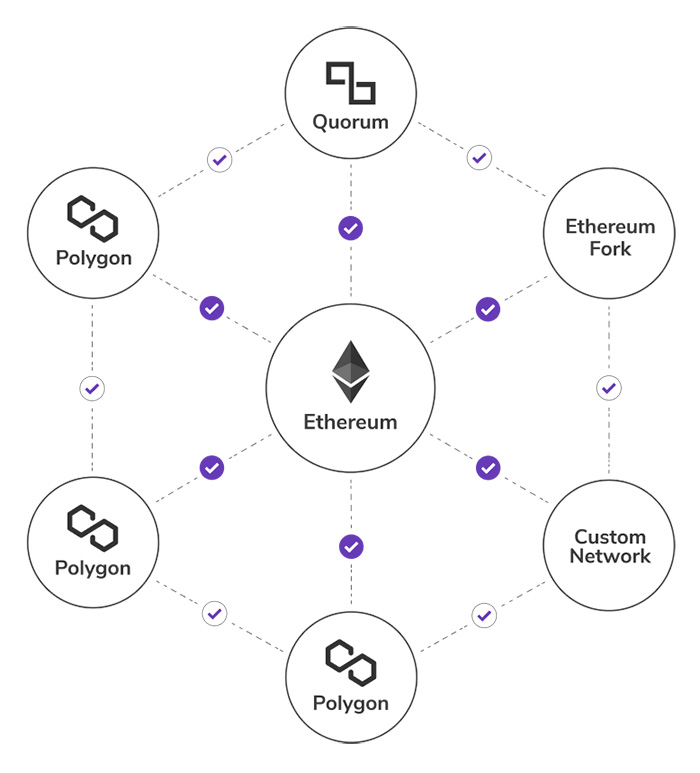
Architecture
The Polygon team has developed a four-layer architecture for the blockchain network: Ethereum layer, security layer, Polygon networks layer, and execution layer. These abstract, composable layers provide the chance for creating specific blockchains that are compatible with Ethereum and connected to each other.
The Ethereum layer is the fundamental layer in the Polygon network that provides the ability to use Ethereum blockchain for Polygon chains. In simple terms, Polygon chains can use the Ethereum blockchain to host and execute the critical components of their logic. The Ethereum layer in the Polygon blockchain is a set of Ethereum smart contracts that manage Finality, staking, dispute resolving, and message relaying.
As the name implies, the security layer in Polygon provides validators that check the validity of Polygon chains. Developers can deploy the security layer in different ways. One of the easiest ones is to implement it directly on Ethereum and benefit from Ethereum miners’ activity.
The third and fourth layers of architecture in the Polygon network are specific to sovereign blockchains. Every activity on a stand-alone or secured chain is managed in these two networks. Transaction processing, consensus, block production, and execution are specific to two top layers.
Is Polygon (Matic) a Good Investment?
Polygon has shown big capabilities and potentials in creating an ecosystem for Ethereum-compatible blockchains. There are many hopes for the future of this blockchain because it can solve many challenges dApp developers face today. The MATIC token of the blockchain experienced a considerable price rise in 2021.
But the future is still not fully bright. The project has to attract more developers and users. Besides, the coin price relies on many metrics, Ethereum success, for example. As a whole, we can predict Polygon to return good rewards for those who consider it as a long-term investment.
Because projects that aim to solve real-world problems and have experienced development/advisor teams mostly giant attraction over time.
Conclusion
Solving the challenges of the blockchain industry is an ambitious plan. Those blockchains that focus on this part of the industry have to be very consistent and patient in their path.
Polygon is a project with goals for solving big challenges. With a considerable history of solutions, the blockchain can become a best-of-its-kind in terms of connecting blockchains and improving the Ethereum vision as a whole.
Decentralization next to sovereign features and easy-to-use tools is a valuable benefit that Polygon offers. If the team becomes successful in attracting more developers, we can expect bigger achievements for the Polygon community.
Project Websites
- Web: https://polygon.technology/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/maticnetwork
- Discord: https://discord.com/invite/XvpHAxZ
- Telegram : https://t.me/maticnetwork

